AI in fintech sector is becoming a necessity and not just a benefit. The industry is moving from automation to augmentation, where AI is not only streamlining procedures but also radically altering the way financial decisions are made. Real-time fraud detection, creditworthiness assessment that goes beyond conventional models, and personalization of financial services at scale are raising the bar for startups and established organizations alike.
Fintech start-ups see it as a leveller. Even a small company can compete with established players in credit underwriting, fraud detection, or algorithmic trading through machine learning models that continually improve themselves. On the other hand, AI is seen by enterprise financial firms to be the next step in achieving legacy systems optimization, risk reduction, and generating new revenue streams.
The question is no longer whether AI has a place in the financial services industry-it is about how fast companies can go down the AI highway without missing the point of trust, security, and regulatory compliance. In this blog we will look at growing market trends, compelling business use cases and potential challenges of AI in fintech.
The growing market for AI in fintech
The AI in fintech market is growing at a fast pace, mainly driven by the rising investments and demand for intelligent automation. In 2023, financial services firms spent $35 billion on AI, with projected investments across banking, insurance, capital markets and payments businesses expected to reach 126.4 billion by 2028.
With this sizeable investment, financial services are one of the most heavily invested industries in AI, with prominent use cases across the enterprise where automation and machine learning are streamlining tasks, reducing operational costs, and improving accuracy.
Much of this investment is targeted at backend AI applications, including fraud detection, compliance automation, and predictive analytics. However, financial leadership is increasingly using AI for more revenue growth – 70 percent of financial services executives believe that AI will contribute to revenue growth directly in the coming years.
The business use cases for AI in fintech
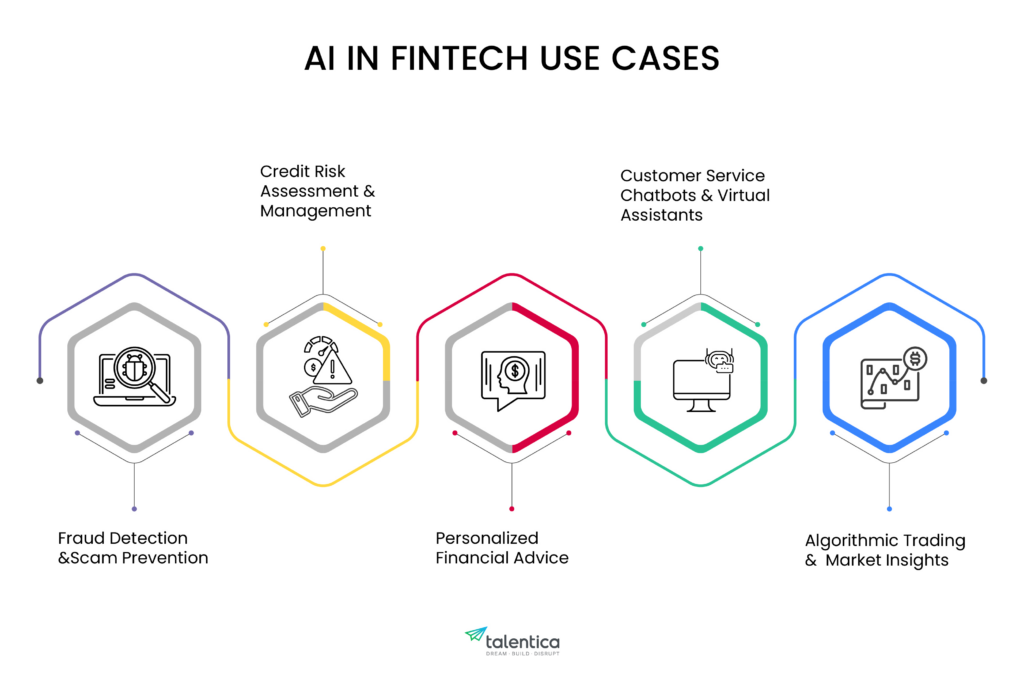
Fraud detection and scam prevention
Fraud is a persistent challenge in the financial sector. Traditional fraud detection systems relied on static, rule-based systems, informing users when a transaction crossed a threshold or originated from an unknown location. However, fraudsters quickly adapted, creating transactions that were barely detectable. AI changes this dynamic by identifying behavioral anomalies rather than just rule violations.
Machine learning models examine millions of transactions in real time to identify fraud before it happens. AI takes context into account rather than rejecting a transaction based solely on its size: Has this consumer traveled recently? Does he or she frequently shop at international stores? Through behavioral analysis, AI can more accurately distinguish between legitimate and fraudulent transactions.
With 90% of U.S. companies reporting cyber fraud in 2024, the stakes are very high. AI-powered fraud detection is not only about security but also about keeping the trust of customers intact. A false positive that mistakenly flags a legitimate transaction can infuriate customers and send them running to competitors. AI cuts down on such friction points and ensures security without sacrificing user experience.
Financial institutions have already invested huge amounts in AI-driven fraud prevention. In 2020, firms spent more than $217 billion on AI applications that would prevent financial crimes. And the investments are on a growth trajectory. Real-time fraud detection is now an expectation, not a differentiator.
Credit risk assessment and management
Credit assessment is another area where AI is redefining what’s possible. Traditional credit scoring models are rigid, often excluding individuals and businesses with thin credit histories. AI is changing this paradigm by expanding the range of data points used to assess creditworthiness.
Instead of relying solely on past credit behavior, AI models assess real-time income trends and spending habits. In some cases, it looks at other sources, such as mobile payments or online purchases, allowing lenders to make more informed credit decisions and give access to previously underserved communities.
In April 2024, Zest AI launched its machine learning algorithms that can make better credit risk forecasts by examining hundreds of variables rather than a few. The end result? More inclusive lending, reduced default rates, and a faster, more accurate underwriting process.
For startups in the lending space, AI offers a chance to compete against traditional banks with faster and more accurate lending decisions. For large financial institutions, AI reduces the risk and increases loan approval rates for qualified applicants. The old credit scoring models are no longer enough—the future is AI-driven assessments.
Personalized financial advice
AI in fintech is not limited to risk mitigation, but also about delivering smarter, more intuitive and responsive financial experiences. Wealth management is no longer limited to high-net-worth individuals. Robo-advisors use artificial intelligence to offer automated and individualized investment solutions, democratizing financial planning.
In 2023, TIFIN introduced an AI-powered platform that offers hyper-personalized financial planning, transforming wealth management from a one-size-fits-all paradigm to something more akin to a personal CFO for each investor.
Customer service chatbots and virtual assistants
Financial services have always been reactive — customers seek out loans, investment advice, or fraud resolution when they need them. AI is making these services more proactive by predicting customer requirements before they arise.
AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants are increasingly handling everything from simple questions to complex financial planning. These systems do more than just answer queries; they also understand context, examine past exchanges, and offer intelligent suggestions. If a consumer consistently saves a percentage of their income, AI can recommend more efficient savings solutions. If spending patterns indicate a potential cash flow problem, AI can suggest financial solutions in advance.
For fintech startups, incorporating AI-powered customer interactions from the start can set them apart. Meanwhile, enterprises can use AI to scale customer support while maintaining personalized interactions. According to studies, AI-powered chatbots can handle more than 70% of customer queries, allowing human agents to focus on more complex issues, thereby increasing overall efficiency and reducing costs.
Algorithmic trading and market insights
AI is changing the way financial firms approach trading and investing. AI-powered algorithmic trading can make fast investment decisions by analyzing past data, current market conditions, and even sentiment from news and social media.
JP Morgan has already integrated AI into its predictive analytics to forecast price movements and market trends and enable proactive trade execution. AI-powered trading algorithms can complete deals faster than a human thanks to real-time market responses. The results include better risk-reward strategies, smarter investment decisions, and improved portfolio performance.
For hedge funds and investment firms, AI is no longer an experimental tool—it’s a necessity. The ability to handle massive volumes of unstructured financial data gives AI-powered trading systems a competitive advantage over human analysts. As AI models develop, their ability to recognize trends in market behavior will only increase.
Also Read: How we helped our client build feature-rich products that simplify complex investment decisions using various AI models. Read full case study!
Overcoming challenges of AI in fintech
But implementation of AI isn’t without its challenges. Fintech companies must address:
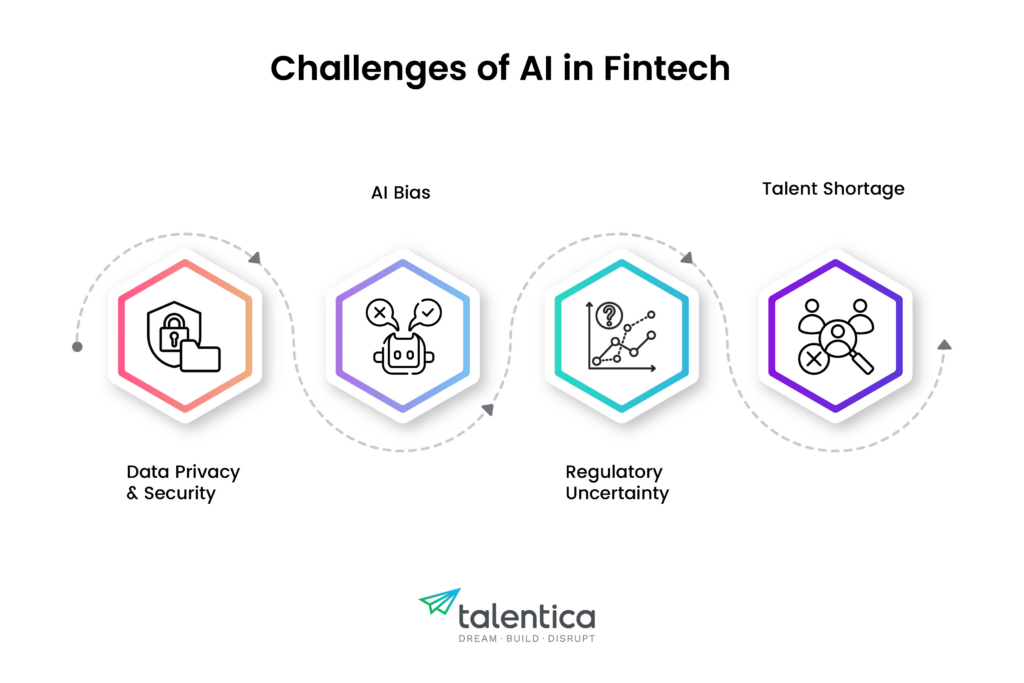
Data privacy and security
AI models are data-hungry and demand massive volumes of information to learn and function at optimal levels. However, financial firms handle extremely sensitive data of their customers, so privacy and security are critical. GDPR, CCPA, and other regulations set strict standards for data collection, storage, and use.
A security breach, even an accidental one, can lead to severe regulatory fines, considerable financial losses, and irreversible damage to consumer trust. As a result, comprehensive data governance frameworks, enhanced cybersecurity measures, and ongoing compliance monitoring are required for responsible AI adoption. This includes approaches to anonymization, differential privacy, and secure data storage.
AI bias
The performance of the AI model depends on the data on which it is trained. The AI system can reinforce and even worsen societal biases if the data reflects them. Biased behavior can result in areas such as fraud detection, insurance pricing, loan acceptance, and credit scoring.
For example, certain demographic groups may be unfairly denied credit if a model based on historical loan data underrepresents them. The variety and representativeness of data must be carefully considered to address AI bias.
Fintech companies must invest in creating a variety of data sets, use fair AI algorithms, and regularly test their models for bias. Explainable AI (XAI) techniques can also help understand a model’s decision-making process, making it easier to identify and remove bias.
Regulatory uncertainty
The legal landscape governing AI in the fintech sector is constantly changing. Regulators around the world are trying to get a handle on this rapidly changing technology. New rules and laws are being created every day, leaving fintechs in the dark.
For companies to be compliant and take full advantage of AI, they must keep up with all of these regulatory developments. This requires keeping an eye on changing regulations, engaging with lawmakers, and developing flexible compliance systems. Developing in-house expertise in AI regulatory matters and ethics is critical to success in this challenging environment.
However, if you don’t have in-house staff with knowledge of the current AI regulatory environment, outsourcing to the right fintech software development company can be a good option. These external teams have up-to-date knowledge of the changing regulatory landscape and can offer tailored solutions to ensure compliance and reduce risk.
Talent shortage
Finding the right people is a major additional issue. AI in fintech requires a very specific set of talents. You need experts in machine learning, data science, statistical modelling and financial analysis, as well as expert teams who understand the intersection of these disciplines.
Globally, there is a talent shortage around the world. According to a recent Salesforce survey, 60% of public sector IT professionals cited a lack of artificial intelligence (AI) skills as their top barrier to implementing AI. Outsourcing can serve as a vital bridge while companies develop their own talent.
Partnering with companies offering AI development services can help fintechs to quickly access the expertise they need, particularly for short-term projects or niche applications. This can accelerate AI adoption and allow companies to gain real-world experience before investing in a full in-house staff.

Conclusion
Financial services companies are among the most data-intensive corporations in the world. Every transaction, risk assessment, customer interaction, and compliance check provide important insights. AI’s strength lies in its ability to leverage and act on this data in real time.
As AI advances, the next frontier will include small language models, Multi- AI agents, and quantum computing. Financial services firms that integrate these innovations early will gain a significant advantage.